2.2.2.3 Quantile / Quartiles
- Quantile : inverse cdf / percent point function (ppf)
- q's quantile
- q's quantile
- Quartiles
- 日本語では、四分位点(しぶんいてん)という。
- Example
is 95% interval.
2.2.3 joint distribution / 2.2.4 independence etc
- Joint distribution
- Conditional distribution
- product rule :
- (unconditionally) independence / marginally independence
- conditionally independence (CI)
2.2.5 Moments of a distribution
- mean / expected value
- for discrete rv :
- for continuous rv :
- for discrete rv :
- variance (often denoted by
- standard deviation :
- The variance of product of
2.2.5.4 Conditional moments
- law of iterated expectations / law of total expectation
- derivation
- Example : Lightbulb
- Factory 1 supplies 60% bulbs, lifetime
- Factory 2 supplies 40% bulbs, lifetime
- Factory 1 supplies 60% bulbs, lifetime
2.2.6 Limitation of Summary Statistics
2.3 Bayes' rule
- Bayes' rule
- For unknown (hidden) quantity
- Given some observed data
- For unknown (hidden) quantity
- Details
- Posterior
Example 1 : Testing for COVID-19
- Notation
- Aim
- calc
- calc
- calc
- Assumption (based on NYC situation in Spring 2020)
- Likelihood
- Sensitivity
- Specificity
- Sensitivity
- Prior (of infection) :
- Likelihood
(Cont.)
- calc
- calc
Example 2 : The Monty Hall problem
- Game flow
- There 3 doors : No.1, No.2, No.3
- A single prize has been hidden behind one of theme.
- At first, you choose a door (suppose door 1)
- Gameshow host opens one of the other two doors (suppose door 3)
- no prize behind it
- You can change your choice (door 1 or door 2)
- There 3 doors : No.1, No.2, No.3
- Problem : Should you
- (a) choose door 1 ?
- (b) choose door 2 ?
- (c) or no difference
(Cont.)
- Notation
- Assumption
- Prior :
- Likelihood
- Prior :
(Cont.)
- After observed
(Cont.)
- Finally:
- You sholud change your choice to door 2!
2.4 Bernoulli / Binomial distribution
- Bernoulli :
- Binomial :
2.4.2 Sigmoid function
- Sigmoid function :
- Sigmoid function + Bernoulli
- predict probability given some input
- predict probability given some input

Logistic regression
- using linear predictor :
2.5 Categorical / Multinomial
-
Categorical :
- In other word :
-
Multinomial :
Softmax / Multiclass Logistic
-
Softmax (or multinomial logit)
-
Multiclass Logistic regression
- Using
- Using
2.5.4 : Log-Sum-Exp trick
- Softmax :
- "exp" value overflows on a computer when
- "exp" value overflows on a computer when
- Log-Sum-Exp trick : Use
- lse function
2.6 Univariate Gaussian (normal)
- Recall : cumulative distribution dunction ; cdf
- Gaussian distribution (cdf)
- using
(Cont.)
- Recall : probability density dunction ; pdf
- pdf of Gaussian
- moments
- mean :
- variance :
- mean :
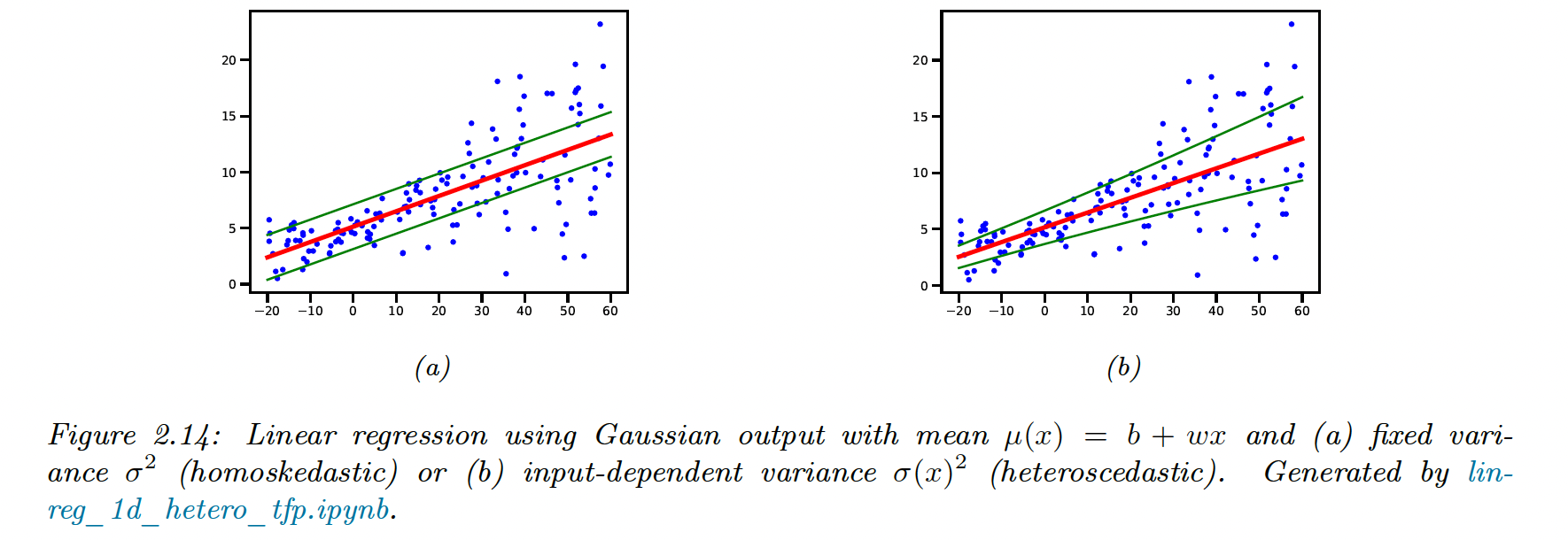
2.6.3 : Regression
- Normal distirbution conditioned on input variables
- Homoscedastic regression (Linear regression)
- Heteroskedastic regression